Planning for a Resilient Future
Wildfire remains the top-rated hazard to life, property, and critical infrastructure within and around the Bow Valley.
The Town of Canmore, in partnership with the Municipal District of Bighorn and Kananaskis Improvement District, and with support from Alberta Forestry and Parks, was successful in its application for funding from the Forest Resource Improvement Association of Alberta (FRIAA) Community Fireguard Program. With FRIAA’s funding, we are now ready to begin construction on the Bow Valley Community Fireguard.
The information on this page outlines the short-term and long-term work required to build a fireguard that will span from the East Park Gates to Dead Man’s Flats, impacts to residents and visitors—including trail closures, smoke in the air, and changes to the landscape, and details about how a fireguard can help to protect our community and support the ecological integrity of the environment.
Bow Valley Community Fireguard: Phase 2
Here is What is Happening
Construction of Phase 2 of the Bow Valley Community Fireguard is scheduled to begin on August 18, 2025 at Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park (CNC). Separated into three distinct areas, work at the CNC will occur at the east end (upper and lower) and at the west end of the park to the boundary of Banff National Park. Similar to Phase 1 (Stoneworks Creek, Harvie Heights, and East Park Gates), construction at the CNCPP will be a blend of mechanical harvesting, hand-crew clearing, and hand-crew thinning.
Work is scheduled to begin on August 18, 2025 (after the restricted activity period as defined by the migratory bird convention act) and will run through to the end of March 2026. Debris pile disposal will occur during the winter of 2026/27.
At the same time as construction begins on the fireguard, Alberta Parks will begin work on targeted fuel reduction to the west of the CNC East (Upper) construction area. While the project has similar benefits to the landscape as the fireguard (i.e. fuel reduction, habitat enhancement) and may appear to look like the fireguard, Alberta Parks’ project is not part of the fireguard’s construction, but rather, in complement to it.
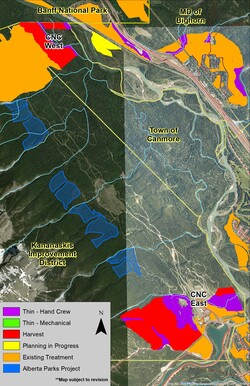
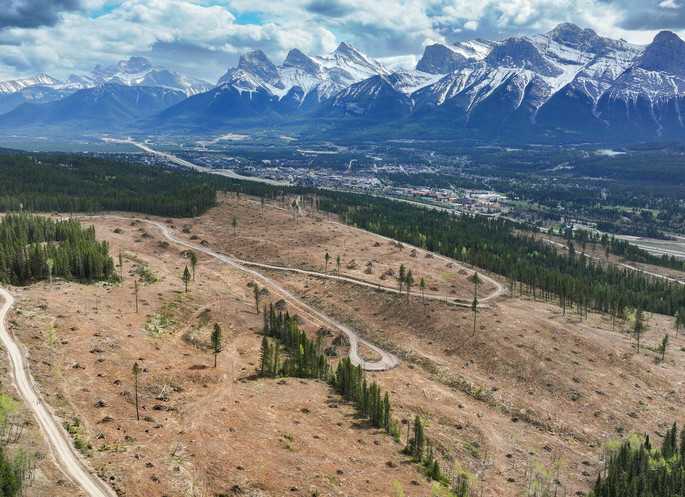
In total, approximately 82 hectares of forest will be harvested and cleared across the Canmore Nordic Centre East (Upper and Lower) and West as part of the fireguard’s construction, with an additional approximate 35 hectares of thinned forest. As with Phase 1, Phase 2 focuses on harvesting lodgepole pine and spruce trees. Deciduous trees and Douglas Fir will be retained. The groundcover will be retained as best as possible.
During Phase 1, 188 hectares of forest were cleared, while 31 hectares were thinned.
For a list of area and trail closures during construction, visit albertaparks.ca/advisories.
To learn about how designated trails in the construction area will be protected, click on the drop-down menu below.
Why Here? Why Now?
Construction of the Bow Valley Community Fireguard at the CNC helps us complete some critical connections of the fireguard across the Bow Valley. Work in the CNC East (upper and lower) area will connect with existing treatment areas in the valley bottom and Stoneworks Creek, while work at CNC West helps us tie into the Carrot Creek fireguard in Banff National Park, and fill gaps between existing treatment and the work we completed at East Park Gates and Harvie Heights.
Construction of the Bow Valley Community Fireguard is essential work to increase Canmore’s, Harvie Heights’, and Dead Man’s Flats’ resilience to wildland fire— the top-rated risk for the Bow Valley. Beyond the municipalities themselves, construction of the fireguard also helps to protect and maintain assets at the Canmore Nordic Centre Provincial Park, like the world class skiing, biking, disc golfing, and training facilities used by everyone from the beginner to the Olympic champion.
Changes to the Landscape
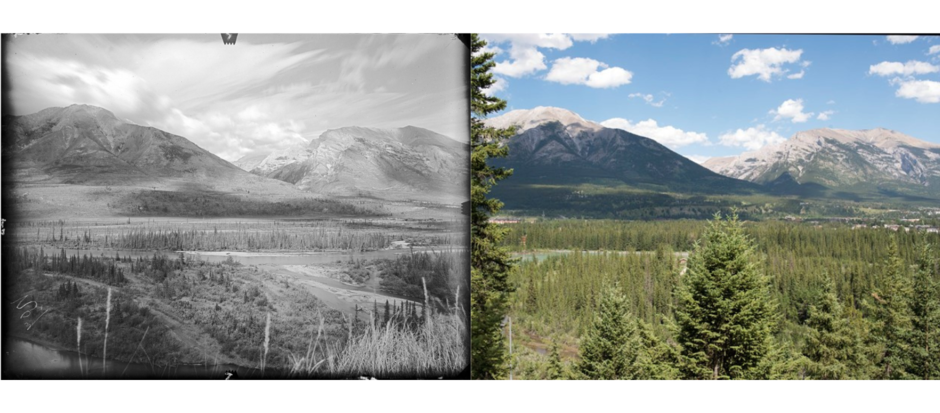
Over a century of wildfire suppression in the Bow Valley has led to unnatural nature. Without regular fire cycles to help open the canopy, regenerate growth, and support the ecosystem, our landscape has transformed into dense, mature, continuous forests with an abundance of fire-prone trees that have lived well-beyond their typical lifespan.
Building a fireguard requires that we remove the fuels (trees, brush, etc.) that encourage the spread of wildfire toward property, critical infrastructure, and lives. As construction on the fireguard is completed, residents and visitors should expect to see a significant break in the forest where trees have been removed.
What to Expect
Crews will focus harvesting on lodgepole pine and spruce trees. Deciduous trees will be retained as much as possible, and Douglas Fir greater than 30 cm at breast height (1.3 m) will be thinned. Ground cover will not be cleared as part of the work, but it will be impacted by harvest operations.
While the changes to the landscape’s appearance will be different, the work on the Bow Valley Community Fireguard will mimic many of the similar positive impacts that a wildfire would have, like opening the forest canopy, increasing forage, and creating edge habitat.

This project has been designed to leave small retention clusters of trees, which will reduce the visual impact of the work.
The impact of harvesting will be most evident in the first year of work; however, it will not take long for vegetation to regenerate, making the construction much less noticeable. Maintenance of the fireguard will occur every 15 – 20 years.

The construction of the Bow Valley Community Fireguard will significantly increase the resiliency of our community when it comes to fighting wildfires and protecting life, property, and critical infrastructure. While the benefits of the fireguard are clear, we know that some residents and visitors may grieve the appearance of the landscape because of the changes that we are making in order to increase our collective safety. We want to acknowledge how much the landscape contributes to people’s sense of belonging and place.
Additional Project Information
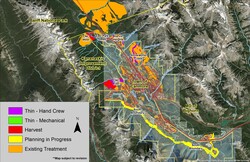
To help protect Canmore and the surrounding areas from wildfire, a fireguard from the East Park Gates to Dead Man's Flats will be constructed in phases over a period of three to five years. Construction of the fireguard will use a combination of mechanical tree removal and forest thinning. While the fireguard will protect the Hamlets of Harvie Heights, Dead Man's Flats, and the Town of Canmore, the majority of the work will be completed on provincial land.
The treatment areas shown on the map were selected as locations that will best help slow the progress of a future wildfire, locations where work is feasible and accessible, as well as locations that augment and complete ongoing previous work, like FireSmart vegetation management and fuel reduction.
| Bow Valley Community Fireguard Work Schedule This schedule and associated maps are subject to change |
|
| Fall 2024 and Winter 2025 | Stoneworks Creek, Harvie Heights, and East Park Gates |
| August - October 2025 and 2026 | Canmore Nordic Centre East and West |
| August - April 2025 and 2026 | South West, South Central, and South East Canmore to Dead Man's Flats |
Mature, continuous forests are not good habitat for an array of species, especially ungulates (e.g. deer and elk) and bears. By harvesting and thinning trees, the fireguard will open the forest canopy and improve the habitat conditions for decades to come by increasing forage and providing edge habitat.
Harvesting may result in a short-term displacement for wildlife, but this will be exceeded by the long-term habitat enhancement. To ensure the integrity of the construction of the fireguard and its impact on wildlife, specialists in human-wildlife coexistence have been engaged in the planning of this project, and a wildlife and avian survey was completed to account for migratory and cavity-nesting birds. The survey identified several potential pileated woodpecker nests on the edge of the fireguard area; these trees will not be removed.
You can read the survey in our list of related links at the bottom of the webpage.
This project is in line with the recommendations from the Human Wildlife Coexistence Report and from the Human Wildlife Coexistence Roundtable.
Natural Resources Canada notes that after a wildfire, forest generation begins with the establishment of pioneer species such as aspen, white birch, and lodgepole pine. All of these species require full sunlight to thrive, and all are well-adapted to landscapes where fires regularly occur.
Aspen and birch can re-establish quickly by sprouting from stumps and the roots of burned trees. These species recolonize burned sites by producing abundant seeds that can be windblown over long distances.
Lodgepole pines depends on fire to regenerate because they have serotinous (protected by a waxy coating) cones that require extreme heat to release their seeds. Wildland fires produce favourable conditions for these seeds to germinate by:
- releasing nutrients in the soil
- exposing mineral soil
- eliminating competing species
- increasing the amount of sunlight on the forest floor
We have selected a contractor for this project whose operators have significant familiarity with designated trails. All designated trails have already been flagged, maps of the trails are reviewed in pre-work meetings, and each operator has a copy of the block map with critical features and trails identified.
Wherever a construction road crosses a designated trail, our contractor will attempt to meet the grade of the trail so there is no cut or fill required. Additionally, the contractor will use a form of protection (e.g. swamp mat, geotextile wrapped logs, etc.) to protect the tread and help with clean reclamation.
To help protect the trails from future blowdown (trees or trees felled or broken off by wind, snow, ice or age), our contractor will not leave any tree buffer zones alongside trails.
Fire Guard
A fireguard is a strategically located break on the landscape where fuels, such as trees, brush or leaves have been removed. This gap in forest canopy fuels can help slow a wildfire and provide safe and strategic locations for firefighters to respond. Proactively built fire guards increase protection and minimize impact to lives, property, critical infrastructure, and the environment.
It is important to know that a fireguard does not prevent a wildfire.
FireSmart™
FireSmart™ Canada is a community wildfire protection program. Examples of FireSmart™ work include removing shrubs, trees, deadfall or woodpiles within the first 10 meters of a building (zone 1). FireSmart™ can also include thinning and pruning of trees in other zones.
What we have grown to see as a natural landscape in the Bow Valley --an abundance of mature trees and decadent forests-- is not a natural landscape at all. Decades of wildfire suppression has resulted in a human-made environment that poses a great threat to Canmore and the surrounding communities; wildfire spreads more quickly and intensely through mature forest. Compounding the dangers posed by a mature forest, Bow Valley communities are developed well into the wildland-urban interface, meaning that there is little to no separation between development and the forest.
The Bow Valley used to see wildfires on a more regular basis, but it has been over 100 years since the last wildfire came through. If we do not manage our forests, nature will manage them for us.
Questions and Feedback
Do you have feedback on or questions about this project? We want to hear from you. Send us an email to fireguard@canmore.ca






